What’s IoT?
IoT stands for “Internet of Things.” It refers to a network of physical objects or “things” that are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to connect and exchange data with other devices and systems over the internet. The primary goal of IoT is to enable these objects to collect, analyze, and communicate data, often without requiring direct human intervention.
Uses of IoT
- Smart Homes
IoT enables homeowners to connect and control devices such as thermostats, lights, security cameras, and appliances remotely. It offers features like energy savings, home security, and voice-activated commands through virtual assistants like Amazon Alexa and Google Assistant.
- Wearable Devices
Fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitoring devices use IoT to track health metrics, such as heart rate, sleep patterns, and physical activity. They provide real-time feedback and allow users to set health goals.
- Healthcare
In healthcare, IoT devices and sensors are used for remote patient monitoring, medication adherence, and early disease detection. It can help improve patient outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions.
- Industrial IoT
Manufacturing and industrial sectors use IoT for predictive maintenance, quality control, and real-time monitoring of equipment and production processes. It increases operational efficiency and reduces downtime.
- Agriculture
IoT sensors and devices are deployed in agriculture for precision farming. They monitor soil conditions, weather, crop health, and livestock. Farmers can optimize irrigation, reduce resource usage, and improve crop yields.
- Smart Cities
IoT is used in urban environments for traffic management, waste management, smart lighting, and public safety. It can reduce traffic congestion, lower energy consumption, and enhance city services.
- Retail
Retailers use IoT for inventory management, supply chain optimization, and enhancing the shopping experience. It includes technologies like RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) and beacons for tracking products and personalizing marketing.
- Logistics and Transportation
IoT devices in logistics and transportation help track shipments, monitor vehicle conditions, and optimize routes. This reduces fuel consumption, improves delivery times, and enhances supply chain visibility.
- Environmental Monitoring
IoT sensors are used to monitor environmental conditions such as air quality, water quality, and weather patterns. This data is crucial for climate research, disaster prediction, and pollution control.
- Energy Management
IoT solutions are employed for efficient energy management in buildings and industries. Smart meters, for example, help monitor and control energy consumption, leading to cost savings and reduced carbon emissions.
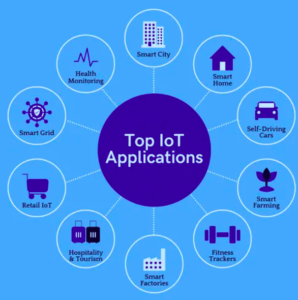
Features of IoT
- Connectivity
This devices are connected to the internet or other networks, allowing them to communicate with each other and exchange data. This connectivity enables remote monitoring and control of devices and systems.
- Scaling
This systems can scale to accommodate a large number of devices and data sources. Whether it’s a few sensors or millions of devices, this platforms are designed to handle scalability.
- Sensing
This devices are equipped with sensors that can collect various types of data, such as temperature, humidity, motion, and more. These sensors enable devices to gather information from the physical world.
- Analyzing
This platforms and applications analyze the data collected by sensors to derive insights and make informed decisions. Data analytics is a crucial component of IoT to extract valuable information.
- Artificial Intelligence
AI plays a significant role in IoT. Machine learning and AI algorithms are used to process data, predict outcomes, and automate tasks. This enhances the intelligence and capabilities of IoT systems.
- Smaller Devices
IoT devices are often designed to be compact and energy-efficient. This allows them to be deployed in various environments, including small and constrained spaces.
- Dynamic Nature
IoT systems are adaptable and can respond to changing conditions. They can adjust parameters, settings, or actions based on real-time data and events.
- Active Engagement
IoT systems actively engage with the environment and respond to triggers or commands. For example, smart thermostats adjust temperatures based on occupancy and preferences.
- Integration
IoT integrates with existing systems and technologies. It can seamlessly connect with other applications, platforms, and databases to share and utilize data.
- Automated
Automation is a core feature of IoT. It allows devices to perform tasks automatically without human intervention. For example, industrial machines can self-diagnose and schedule maintenance.
- Security
Security is a critical feature of IoT, as connected devices and data are susceptible to cyber threats. IoT systems incorporate security measures to protect data and devices from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Endpoint Management
IoT systems require efficient management of endpoints (devices). This includes tasks like device provisioning, updates, monitoring, and troubleshooting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Internet of Things (IoT) is a transformative technology that has brought about significant changes across various industries and aspects of daily life. Its core features, including connectivity, scalability, sensing, analyzing, and integration, have paved the way for innovation and automation. IoT devices, often small and energy-efficient, actively engage with the environment and can adapt to dynamic conditions.
FAQS
1.What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects, devices, and sensors that are connected to the internet or other networks. These objects can collect and exchange data, enabling them to interact with each other and with humans.
2.What are some common examples of IoT devices?
Common examples of IoT devices include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, connected home security systems, smart refrigerators, industrial sensors, and even autonomous vehicles.
3.How do IoT devices communicate with each other and the internet?
IoT devices use various communication technologies, including Wi-Fi, cellular networks, Bluetooth, Zigbee, and LoRaWAN, to connect to the internet or other devices. The choice of communication method depends on factors like range, data requirements, and power consumption.
4.What are the main benefits of IoT?
The main benefits of IoT include increased automation, improved data-driven decision-making, enhanced efficiency, cost savings, and the ability to monitor and control devices remotely. It can also lead to innovations in various industries.
5.How is data collected and processed in IoT?
IoT devices collect data from sensors and send it to cloud-based platforms or edge computing devices. Data is processed and analyzed using algorithms and machine learning to extract insights and trigger actions.